Home | Industries | Governments | The NextLabs Approach to CISA’s Zero Trust Maturity Model (ZTMM)
Purpose of CISA and the Zero Trust Maturity Model (ZTMM)
The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) is a federal agency within the United States Department of Homeland Security (DHS) that plays a vital role in protecting the nation’s critical infrastructure and ensuring the security of cyberspace. CISA’s Zero Trust Maturity Model (ZTMM) was first published in 2021 and supports the U.S. government’s modernization and cybersecurity objectives outlined in several executive orders and documents.
- Executive Order (EO) 14028: “Improving the Nation’s Cybersecurity” by requiring federal agencies to adopt a Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA). It also aims to enhance collaboration between government and the private sector to secure digital environment for the United States.
- OMB Memorandum M-22-09: it mandates that all Federal Civilian Executive Branch (FCEB) agencies align their cybersecurity programs with Zero Trust principles by the end of FY2024.
CISA’s ZTMM model provides a structured approach for federal agencies to transition to ZTA and adopt a data-centric security model. It assists agencies in the development of their zero trust strategies and continued evolution of their implementation plans in adherence to principles including “never trust, always verify,” “assume breach,” and “least privilege access.”
ZTMM Pillars and Principles
The ZTMM reflects the seven tenets of NIST SP 800-207, and encompasses implementation ranging across five pillars — Identity, Devices, Networks, Applications & Workloads, and Data. Each pillar contains details to advance manual, siloed processes to fully automated, integrated capabilities in three cross-cutting capabilities: Visibility and Analytics, Automation and Orchestration, and Governance. More details about the pillars and capabilities will be discussed in the following sections.
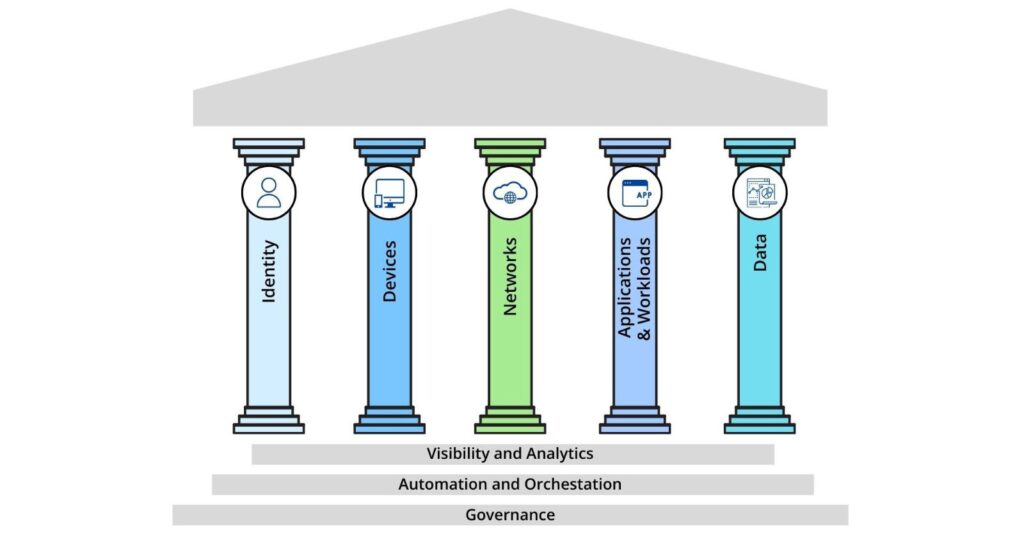
ZTMM Implementation Stages
The progression towards an optimal ZTA and automated process can take different pace in the four pillars depending on the compatibilities of the dependencies within the organization and its enterprise environment. Ultimately, coordination and consistent governance across pillars are crucial to a successful implementation of a ZTA across the capabilities. ZTMM defines the implementation process with four levels of maturity — Traditional, Initial, Advanced, and Optimal — reflecting how an organization evolves from static, manually configured security controls to fully automated, adaptive Zero Trust systems.
- Traditional: Manual and siloed processes with static policies.
- Initial: Early automation and cross-pillar integration.
- Advanced: Coordinated, automated controls with centralized visibility.
- Optimal: Fully automated lifecycle management, dynamic least privilege, and enterprise-wide awareness.
How Can Organizations Use the ZTMM?
Organizations in both public and private sectors can apply the ZTMM to guide their Zero Trust implementation. While organizations used to rely heavily on traditional perimeter-based security, it is no longer sufficient against the modern threat landscape. The ZTMM provides a proactive and adaptive approach to implementing Zero Trust to address some of the most pertinent issues in an era of the Cloud:
- Insider threats: The emergence of remote work and the adoption of cloud computing have expanded the traditional network perimeter and significantly increased risk levels. Through continuous monitoring and context-aware access control, ZTMM provides a structured framework for more granular and comprehensive access controls and identity management practices.
- Regulatory compliance across industries: The ZTMM can serve as a roadmap for organizations to meet stringent standards by providing clear guidelines and best practices for implementing a robust Zero Trust security model.
- Data protection across all environments: whether within on-premises, cloud environments, or on user end points, the ZTMM provides a comprehensive approach to protect sensitive information wherever it resides.
Implementing Zero Trust with NextLabs
NextLabs’ Zero Trust Data-Centric Security solutions are designed to enable organizations to advance through the stages outlined by the ZTMM. NextLabs’ products allow users to balance the need to share with the need to protect by allowing access to an organization’s data, network, applications, and other sensitive assets to be granted or denied dynamically in real-time. NextLabs solutions can help organizations with elements in each of the five pillars and three cross-cutting capabilities that make up the ZTMM.
- Identity: Uses Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) to enforce policies dynamically based on user roles, clearance, location, and context.
- Devices: Incorporates device attributes to prevent unauthorized access, even offline, with centralized monitoring.
- Networks: Enables micro- and macro-segmentation for data-level protection beyond traditional network boundaries.
- Applications & Workloads: Provides centralized, fine-grained access control across applications with consistent policy enforcement and auditing.
- Data: Protects data at rest, in use, and in transit through dynamic policy evaluation and lifecycle protection.
NextLabs also supports all three ZTMM cross-cutting capabilities:
- Visibility and Analytics: Centralized monitoring and auditing provide full traceability of data access and usage, with alerts for anomalous behavior.
- Governance: Fine-grained ABAC policies ensure consistent enforcement of least privilege and data segregation down to the field level.
- Automation and Orchestration: Policies are centrally managed and automatically propagated across enforcement points without code changes, improving agility and reducing human error.
NextLabs’ data-centric dynamic authorization allows organizations to implement the principles of ZTA which are deeply integrated into all NextLabs product lines, including:
- CloudAz, a unified policy platform that centralizes administration and utilizes the “never trust, always verify” principle, ensuring data is protected at any access point.
- SkyDRM ensures persistent protection of critical files and documents to protect data on the move and at rest.
- Application Enforcer which can be used to secure applications, enforce data security controls, and simplify role management.
- Data Access Enforcer (DAE) helps enterprises protect data access from anywhere, by securing access and protecting critical data stored in databases and data lakes.
Key Takeaways
Implementing Zero Trust is essential for countering evolving threats, protecting sensitive data, and maintaining compliance. CISA’s ZTMM provides a practical framework for assessing and advancing Zero Trust maturity, while NextLabs’ Zero Trust Security Suite offers the tools and automation necessary to make that journey achievable. By adopting this approach, organizations can reduce risk, ensure data protection across hybrid environments, and establish a resilient cybersecurity posture.
For more in-depth analysis of ZTMM and how organizations can advance through each stage, read the full White Paper.






